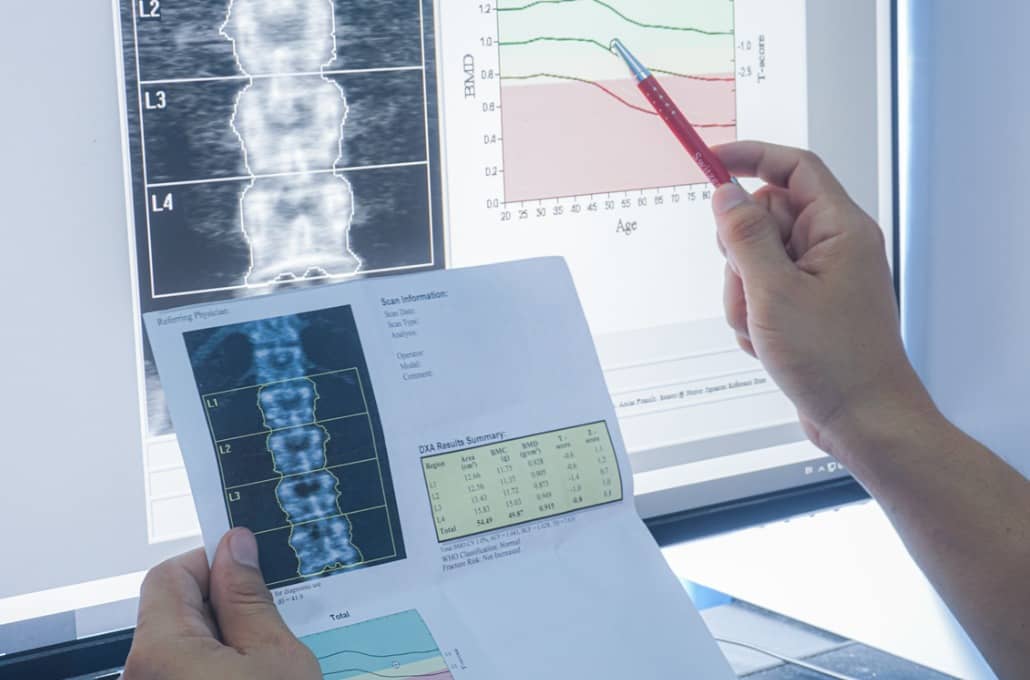
Bone density – what is it?
The density of the bone represents its strength. In bone densitometry (osteodensitometry), we determine the calcium salt content responsible for density. Its value, in conjunction with the age of the patient and the general condition of the bones, allows conclusions to be drawn about the presence of osteoporosis (bone loss).
Arrange online appointment
Quickly and easily get an appointment at a Radiologie München practice in Radiologie München.
Where can you have bone density measured in Munich?
Our specialists offer bone density measurement by QCT at almost all locations. We perform the DXA procedure in our practice at the OEZ in Moosach. Please feel free to ask for an appointment!
For whom is osteodensitometry useful?
From about the age of 50, the strength of the bones naturally decreases. Normally, it decreases by about 1 percent per year. Increased risk is associated with more rapid decline. In women during and after menopause, it is not uncommon for bone density to decrease by 2 to 4 percent. Therefore, bone fractures are more frequent in older women and monitoring of their development is very important.
Other risk factors for the occurrence of osteoporosis are heavy alcohol or tobacco consumption, malnutrition or hyperthyroidism.
Different methods
In bone densitometry, rays penetrate the bone and are attenuated there to varying degrees – depending on the calcium salt content. A comparison of the measured values with the standard values allows us to draw further conclusions.
DXA procedure
DXA stands for “Dual-X-ray-absorptiometry”, the so-called two-spectrum X-ray absorptiometry. In the process, we take digital X-rays of the lumbar spine and hip. Diagnostics with DXA is very accurate, as deviations of only 3 to 4 percent from the average reference values can be shown. The large number of comparable studies in a wide variety of groups of men and women reinforces the message of the measurement.
The radiation exposure during X-ray examination is a fraction of a normal X-ray. The measurement is least stressful.
QCT procedure
Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) produces slice-by-slice images of different areas of the skeleton. X-rays are used to structurally record the interior of the bones. This allows the risk of bone fracture to be assessed very accurately, irrespective of any degenerative changes that may have occurred previously.
However, this examination takes longer than the DXA measurement.
How does a bone density measurement work?
After the introductory conversation with the examining physician, you will be guided to the appropriate equipment room.
The device used for bone densitometry is individually calibrated to your age, height and weight. After removing jewelry and other metallic objects, the examination starts. You should lie very still and respond to instructions from our staff if necessary. After about 20 minutes, the examination is finished and you discuss the results with our team.
How much does this examination cost?
Bone densitometry is not covered by statutory health insurance. This is a so-called individual health service, IGeL for short. The cost is about 40 euros.
Private health insurance companies usually cover the costs.
Sports Medicine
Information on diagnostics for sports-related musculoskeletal injuries
Bone age
Determination of bone age for the diagnosis of growth disorders in children
Musculoskeletal diagnostics
Back to the overview of musculoskeletal diagnostics