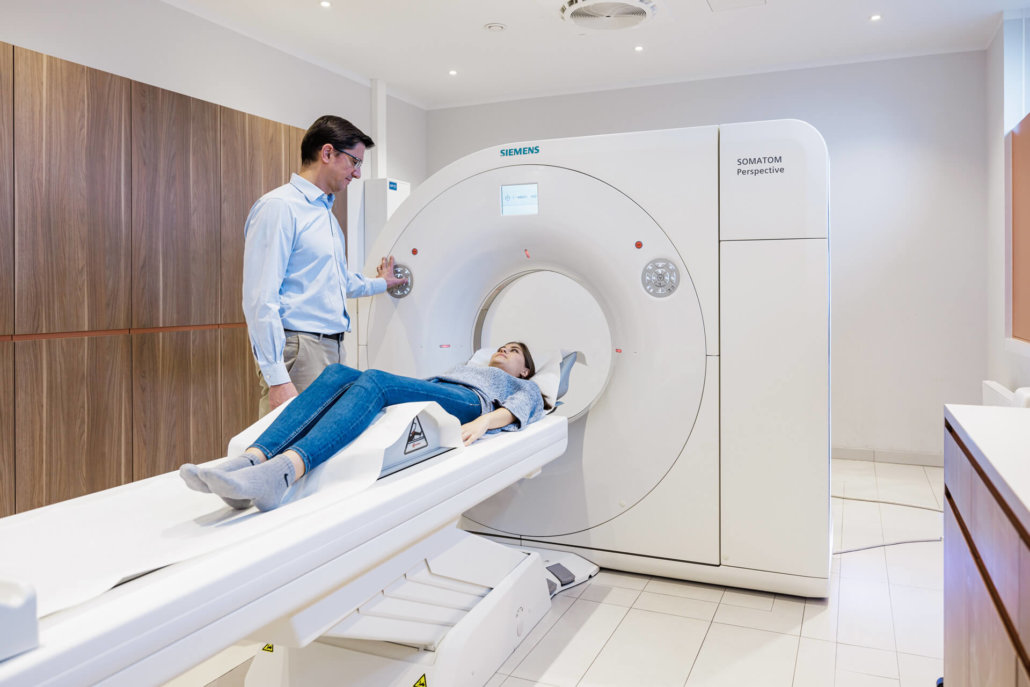
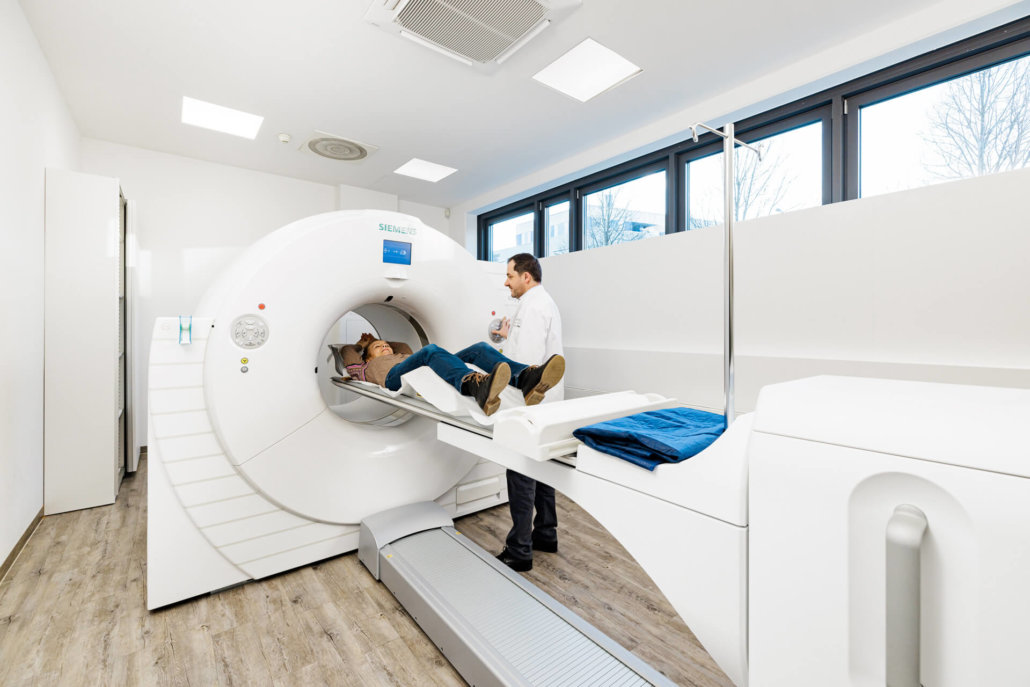
CT without claustrophobia
Claustrophobia in a narrow tube is not an uncommon problem, even among our patients. That’s why we have units with extra-large inner diameters at our sites. In addition, the tubes are very short due to a slim design of the CT units, so that the constriction is as low as possible.
Technical equipment
Innovative high-performance CT equipment from Siemens Healthineers – In addition to standard CT, we also have dual-energy CT, which allows for faster and more accurate exams. On the one hand, this reduces the burden on our patients, and on the other hand, we can use much more effective imaging for accurate diagnoses.
Your CT examination in Munich
During a computed tomography (CT) scan, different body structures are displayed. For this purpose, the patient lies in a rotating X-ray tube. The rays that penetrate his body are attenuated to different degrees depending on the density of the organ. At the same time, the radiation exposure remains very low.
With our modern equipment we offer fast and meaningful results – in all locations in and around Munich.
How does a CT scan work?
Computed tomography (CT) is an imaging technique used to visualize various body structures. During the examination, the patient lies in a rotating X-ray tube. The radiation doses are very low. Depending on the density of the organ or structure, there is greater or weaker attenuation.
For example, bone tissue represents a high-density tissue, which is why it appears bright on the images. Lung tissue, on the other hand, appears dark due to its low density. CT depicts the different body structures, such as the heart, lungs and bones, as shaded images. In a very fine level of detail, changes in the examined tissue can thus be detected quickly.
A slice image is generated for each rotation, which is why a very precise localization of the organ areas potentially to be treated becomes possible. In addition, the CT slice images also allow detailed surgery and treatment planning.
Subsequently, our team of specialists creates three-dimensional images on the computer, which in turn can be used to reconstruct any number of thin images in any sectional plane of the body. Computed tomography allows the size and extent of even the smallest changes in organs to be detected at an early stage, thus providing extremely accurate information about the nature and extent of diseases.
What is examined with a CT scan?
Computed tomography is used to diagnose various diseases and injuries. Depending on requirements, the entire body can be examined using whole-body CT or only specific regions of the body.
The procedure is generally suitable for assessing the skull, neck, thorax, abdomen and pelvis. Furthermore, thanks to state-of-the-art technology, high-resolution imaging of the heart and vessels is possible with a radiation exposure that is significantly lower than conventional catheter angiography. Other applications include dual-energy CT for metal artifact reduction, kidney stone differentiation, or gouty tophi detection, among others. Virtual colonoscopy is also performed using computed tomography and is an alternative procedure to colonoscopy for some patients.
In addition, CT-guided biopsy can be used to perform minimally invasive tissue-sparing sampling as part of the pretherapeutic workup (e.g., for malignancies).
What is the difference between a CT and an MRI?
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are among the most important imaging techniques that produce three-dimensional cross-sectional images of the human body.
Computed tomography
- Fluoroscopy with the help of X-rays
- Lowest possible radiation exposure
- Quiet investigation
Magnetic resonance imaging
- Fluoroscopy with the aid of magnetic fields and radio waves
- No radiation exposure
- Loud knocking noises during the treatment due to the changing magnetic fields
What does PET/CT mean?
PET/CT is the combination of two different imaging examination methods: positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT).
PET uses radioactive substances to make the metabolic activities in the body visible. This allows cancer cells and inflammation to be detected, as they have an altered metabolism compared to healthy cells. The problem with this is that although PET shows the altered cells, the foci cannot be precisely localized because the anatomy of the region being examined is not imaged. This is where CT comes in: CT scans show the patient’s internal body structures (bones, tissues, organs) in high-contrast images.
What should you consider before the examination?
Before the computer tomography, your doctor in charge will discuss the upcoming examination with you in detail and give you the necessary information on how to proceed. Especially if a contrast medium is used for the examination.
Here it is essential to clarify whether you suffer from hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, kidney dysfunction or allergies. For this purpose, a blood analysis is performed in the laboratory, the values of which must not be older than three weeks for the CT scan.
The CT scan itself takes only a few minutes. Nevertheless, you should allow one to two hours for your visit, as the preparation takes some time. Especially if you require oral or intravenous administration of contrast media. This is because it takes a while for the contrast medium to spread throughout your body. If you are given oral contrast medium, you will need to drink plenty of water over the course of an hour. Then the scan takes place in about 15 minutes. These are always done lying down, on your back.
Depending on the issue, you may also be required to hold your breath at the direction of medical personnel. This allows certain body structures to be mapped more precisely. The CT data will then be evaluated and the results discussed with you.
How much does a CT scan cost?
In most cases, the costs for a CT are not covered by statutory health insurance. It is advisable to have a detailed consultation with your doctor. For patients with private health insurance, the costs are often reimbursed.
Radiation exposure
A CT scan involves radiation exposure to the body that is higher than normal X-ray examinations. How high the exposure is depends on the dose administered, which in turn depends on the duration of the examination and the tissue to be examined. For example, the average radiation exposure for an abdominal CT is up to 2.0 millisieverts.
For comparison: In Germany, radiation exposure from cosmic rays averages 2.1 millisieverts per person per year. To avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, you should check with the doctor beforehand whether computer tomography is the right procedure for the examination.
Side effects of the contrast agent
After administration of contrast media, headache, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea or abdominal pain may occur in some cases. Allergic reactions can also occur unexpectedly, but these can be treated with medication.