Dual Energy
more images with less load
Dual-energy computed tomography allows simultaneous acquisition of two CT data sets. Modern examination with different X-ray energies allows more precise tissue differentiation than before. The dose, on the other hand, corresponds to that of a conventional CT scan. The recording takes only a few seconds.
max. 15-30 min
Duration of examination
approx. 60 min
Time in practice
> 90%
Accuracy of the diagnosis of constrictions
At which location can you have dual-energy computed tomography performed?
Two colleagues from the Radiologie München team, Prof. Johnson and Prof. Dr. Graser, have been instrumental in the development of this technology, are internationally known as experts in this field, and have published a large number of scientific papers and several textbooks on it. Our patients are therefore in good hands with dual-energy CT at the Radiologie München sites.
When is a dual-energy CT used?
Dual-energy CT, with its significantly improved differentiation of individual tissue layers, has a wide range of applications. These include:
- Kidney stone differentiation
- Detection of gout tophi
- Detection of silicone from mammary implants
- Metal artifact reduction
- Evidence of bone marrow edema
- Imaging of the pulmonary circulation
- CT angiography without bone overlay
- Differentiation of liver and kidney lesions
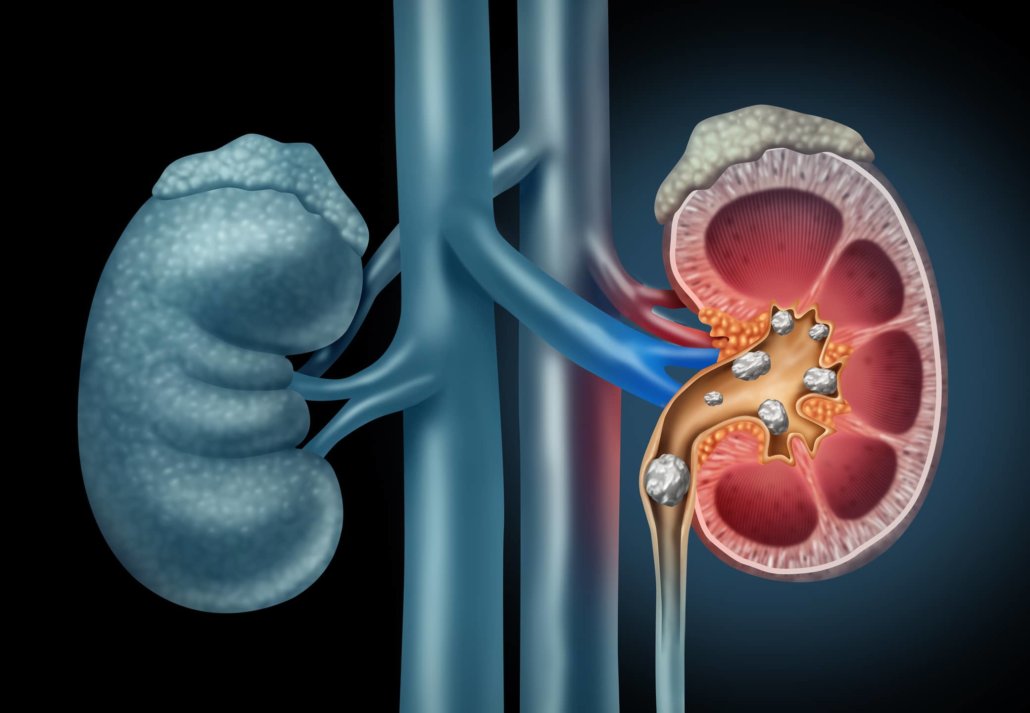
Detection and differentiation of kidney stones
Dual-energy CT allows the detection and typing of kidney stones non-invasively and reliably in a few seconds, even in the presence of obstructed urinary tract. In the case of uric acid stones, drug therapy may be indicated if necessary, and mechanical removal may be planned for other stones.
In addition to calcium and uric acid stones, cystine and struvite stones can usually be differentiated so that appropriate medication, diet, or antibiotic therapy can be indicated. The images show a calcium oxalate stone (blue) in the left ureter and a uric acid stone (red) in the right ureter.
Silicone detection
The technique allows specific detection of silicone in tissue and lymph nodes. Thus, even in non-MRI-capable patients (e.g., with cochlear implant or pacemaker), a complete assessment of mammary implants and, in the case of ruptures, detection of draining lymph nodes is possible. The image shows a ruptured implant whose silicone is being removed into the axillary lymph nodes.
Evidence of bone marrow edema
In trauma diagnostics, only CT offers precise and specific detection of the fracture line, whereas MRI is very sensitive due to the detection of bone marrow edema, e.g., for osteoporotic vertebral fractures or for fissures and fatigue fractures in extremities.
With the dual-energy technique, bone marrow edema is also detectable on CT, thus combining high specificity with increased sensitivity. The image shows bone marrow edema in the lateral femoral condyle.
Differentiation of liver and kidney lesions
In liver and kidney lesions, the contrast image often plays a decisive role in the classification as benign or malignant. In computed tomography, however, only one contrast phase is usually recorded to minimize the X-ray dose. Then it happens that it is primarily not possible to see whether a lesion contains contrast medium, which, for example, in the kidney often makes it impossible to distinguish between hemorrhagic cysts and renal cell carcinoma.
With dual-energy CT, the contrast agent can be detected and displayed in color, so that a clear diagnosis can usually be made in the example given, and without additional contrast agent or additional dose. In the picture shown, the cysts are only hemorrhaged.
Detection of gout tophi
Dual-energy CT can specifically detect gouty tophi even in atypical locations and differentiate them from other erosions or osteolyses. Accurate quantification and follow-up of uric acid depots are also possible with this technique, which allows much more precise control of therapy, e.g. under uricase, compared to serum levels. The picture shows extensive gouty tophi on the right knee.
Metal artifact reduction
In dual-energy CT, metal artifacts can be significantly reduced and usually completely removed in the case of titanium and up to about 1 cm thick in the case of steel, depending on the alloy. This allows a much better assessment of osteosyntheses or the spinal canal.
Loosening of pedicle screws or prosthesis stems or sockets can also be assessed much more reliably due to the artifact-free visualization of the metal-bone interface. The left image shows the standard reconstruction, the right one the result of the metal artifact reduction. The spinal canal becomes assessable and the loosening hems at the pedicle screws are visible.
Imaging of the pulmonary circulation
Along with ventilation of the lungs, blood flow is the most important functional parameter. With the spectral information from dual-energy CT, it is possible to visualize the contrast agent in the lung tissue and thus obtain information about the blood flow. Especially in cases of minor pulmonary embolisms, recurrent embolisms, unclear pulmonary hypertension, and diseases of the lung tissue itself, this information is of great importance for diagnosis and, in some cases, for treatment planning.
Dual-energy CT can also be used to visualize the ventilation of the lungs (see image). However, this requires the use of xenon gas as a contrast agent, which is complex and expensive. Therefore, this application is limited to a few cases mainly in scientific studies. In contrast, imaging of pulmonary blood flow is available in routine images as additional information without additional burden to the patient.
CT angiography without bone overlay
In computed tomography, the arteries in the head and neck region as well as in the trunk and legs can be visualized with high spatial resolution. Until now, one problem has been that calcifications and bones overlay the visualization of the blood vessels and, in some cases, also hinder the measurement of constrictions.
The dual-energy technique can be used to remove calcifications and bone from the data set. This makes it possible to visualize blood vessels without superimposition and also to accurately graduate constrictions. The images show, on the one hand, cerebral arteries white, cerebral veins blue, and, on the other hand, the iliac and leg arteries with vascular calcification but without bone overlay with multiple occlusions.
How does an examination with the Dual-Energy CT work?
Preliminary talk & contrast agent administration
At Radiologie München, every examination is preceded by a detailed preliminary discussion. Our specialists will explain the rest of the computed tomography procedure and the effects of the contrast agent used. In this conversation, you can express your fears about the examination. In the further procedure, a contrast agent containing iodine would be injected via the arm vein. The examination takes place after the injection, lying on the back.
Examination with the Dual-Energy CT
During CT, our patients are then passed through the wide opening of the CT machine several times (depending on the individual examination) – the individual measurements are taken within a few seconds. Any pulse suppression, for example by breathing techniques or beta-blockers, is no longer necessary due to the outstanding image acquisition. In the follow-up consultation, one of our specialists will present the results of the examination.
What are the risks of dual-energy computed tomography?
With dual-energy computed tomography, patients are at very low risk. As with a conventional CT scan, there is radiation exposure and injection of a contrast agent containing iodine.
Radiation exposure risk
The CT scan involves radiation exposure to the body, which is higher than normal X-ray examinations. The amount of exposure depends on the dose administered, the duration of the examination, and the tissue being examined. In any case, dual-energy computed tomography should be performed only when needed by the physician to detect and type specific diseases.
Risk contrast agent
The contrast agent may cause headache, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea or abdominal pain in some cases. Here it is recommended to drink a lot of water after the treatment. If there is no improvement in the near future, you must contact us immediately. Allergic reactions can also occur unexpectedly, but these can be treated with medication.