Persistent joint pain usually indicates inflammation in the musculoskeletal system. Chronic joint disease is often due to rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatism) or osteoarthritis. The inflammation spreads to the joint capsules, muscles, tendons, and bones, leading to persistent pain and restrictions on movement.
rd. 20%
of all Germans suffer from joint pain at some point in their lives
These diseases are now considered a worldwide widespread disease that can affect young and elderly people. In Germany alone, about 10 million people are affected. Because advanced chronic joint disease is not curable, early detection is a critical factor in treating the disease.
Where can you have a pelvic leg screening in Munich?
The area of the leg and pelvis is mainly checked for calcifications of the blood vessels and organ pathways during the screening of the same name. Any blockage can have very serious consequences as a thrombosis. Regular screening brings safety and also the earliest possible diagnosis. This significantly improves the therapeutic options. Ask our specialists for an appointment!

At what point is a preventive examination of the joints useful?
Chronic joint diseases are not curable. If the disease remains untreated, the inflammatory process in the joints continues and the joints become irreversibly damaged. The pain worsens and the mobility of the joints becomes increasingly limited. Often, an affected person does not get checked out until the pain becomes overwhelming. However, by then the disease is already advanced and treatment can only slow down the progression of the disease and relieve discomfort.
For this reason, early detection is of elementary importance. If a person suffers from more than two swollen joints for more than a month, he or she should be examined by a specialist. Rheumatoid arthritis, for example, announces itself early, even before the person visits the doctor because of the symptoms. If treatment begins early enough, severe consequential damage to the joints and the development of chronic joint disease can be prevented.
Early diagnosis of the disease is critical to treat the disease in a targeted and efficient manner. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis both belong to the rheumatic group, but differ in their causes. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease. Inflammation in the joints is caused by overuse or misalignment of the joint. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, results from an autoimmune reaction of the body. The body’s immune system perceives joints as foreign bodies, attacks them and inflames the joint and surrounding structures.
What is the procedure for joint diagnostics?
If a person experiences multiple swollen joints over a six-week period, they should see their primary care physician. She is then referred to a specialist in rheumatology if there is a reasonable suspicion. The specialist first examines the patient’s blood, paying particular attention to certain values such as the inflammatory protein CRP, rheumatoid factor, certain antibodies (ACPA) and uric acid. The primary imaging modalities used are ultrasonography (sonography) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to monitor the condition of the joints.
Ultrasound
Joint sonography allows the physician to visualize fluid accumulation and joint inflammation in the joint. Possible damage to cartilage, muscles, tendons and bones is also made visible.
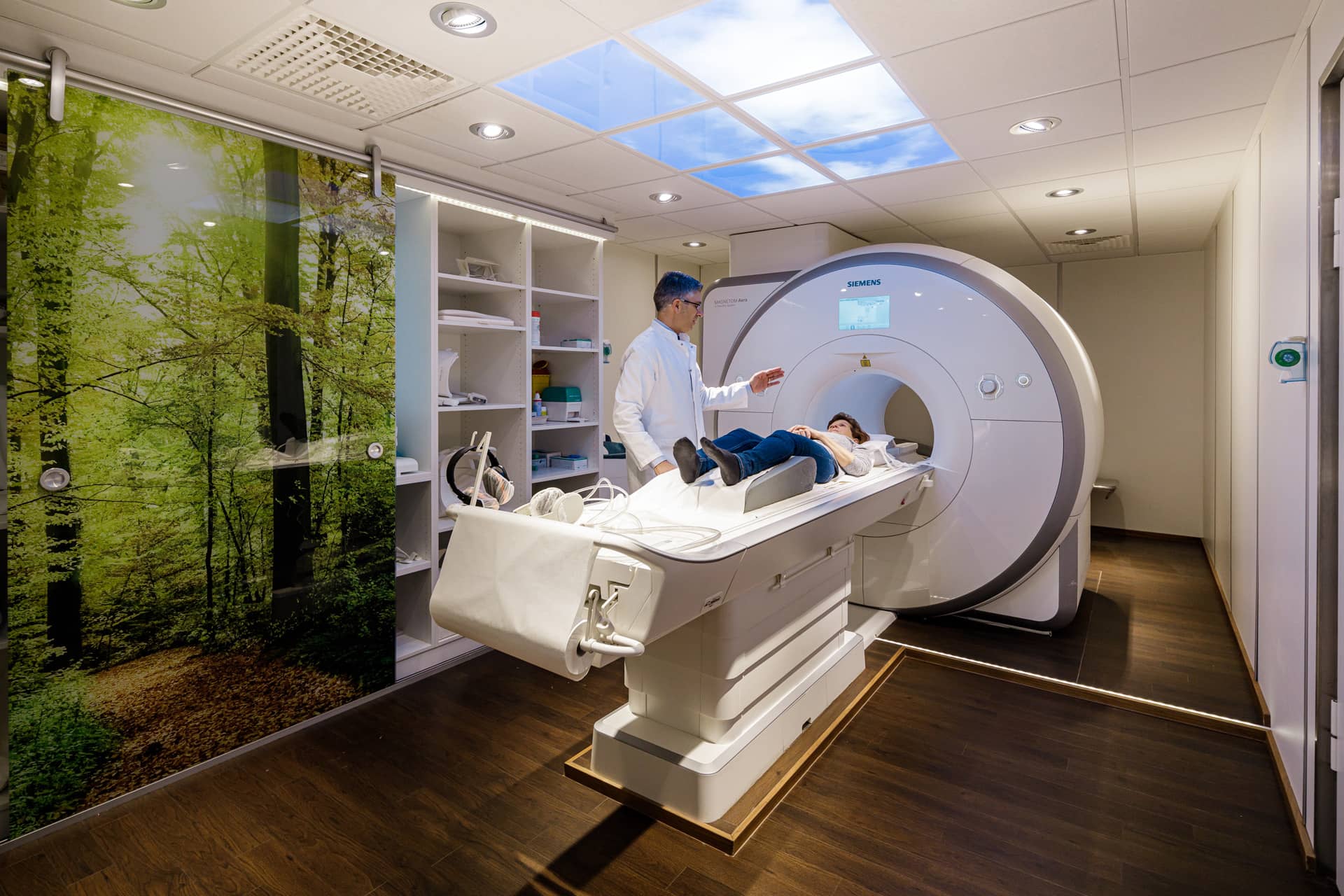
Magnetic resonance imaging
This method makes it possible to visualize changes in the joints at an early stage. In addition, soft tissue structures such as tendons, muscles, bursae and menisci can also be well imaged to detect inflammation. The joint structures are made visible with the aid of radiation-free magnetic waves. For this reason, the examination is well tolerated by many patients.
X-ray
X-rays of the affected joints may be helpful to visualize possible destruction of the joints and bones. At an early stage of the disease, decalcification of joint bones can be visualized, and at a later stage, cartilage wear and bone damage. X-ray examinations are an important imaging procedure, as the success of the treatment or the progression of the disease can be monitored regularly.
What do I need to keep in mind for joint care?
Cost absorption
There is no government-sponsored screening program for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, if the disease is suspected or diagnosed, the statutory health insurance covers the costs of diagnostic and control examinations. Medications and possible surgeries are also paid for by the health insurance. Herbal remedies are only covered by private health insurance if prescribed by a physician. Alternative healing methods, on the other hand, must be paid for by the patient.
To note
Neither the ultrasound examination nor the magnetic resonance imaging are stressful for the patient, as the radiation is harmless. While ultrasound examinations use ultrasound waves, MRI uses magnetic waves.
X-rays, on the other hand, use ionizing radiation to scan the body. Since neither pregnant women nor children should be exposed to radiation, this type of examination should not be used in suspected cases of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Therefore, please inform your doctor early if you are pregnant.